Injection molding or thermoplastic injection makes it possible to manufacture objects in very large series, using the right material. The quality of the mold and the precision of the process make it possible to obtain visual and functional production parts. These series parts are produced for use in many fields. They can be used, for example, for household appliances or in automobiles.
The principle of injection molding
Thermoplastic injection involves injecting a molten polymer (thermoplastic material) under high pressure into a mold through an injection molding machine.
The operation of injection molding
Injection molding uses thermoplastic materials. These exist in the form of pellets before the transformation phase. They are softened under the effect of heat. Once liquefied, the material is injected into a mold and takes the impression of it. It then cools and solidifies. When it achieves its hardness, we can extract the part that becomes usable.
Major stages of injection molding
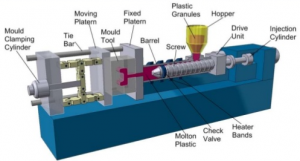
- Making a mold. The mold is composed of two halves, a fixed part, and a moving part. The mold design must allow for the easy ejection of the parts.
- Install the mold in a specific machine: the injection molding machine. The two parts of the mold are strongly pressed against each other. The material (in the form of pellets) is poured into a plasticizing screw (or endless screw) which is heated. The rotation of the screw, combined with the temperature, softens the pellets, which are transformed into the molten plastic material. The molten and deformable material is stored at the front of the screw prior to injection.
- Inject the softened plastic materials under high pressure under the effect of heat in the mold. In this phase, it must be ensured that the mold is completely filled before the material solidifies. This is why we continue to send the material under pressure to compensate for the withdrawal that occurs when the material cools.
- Cooling of the whole through cooling channels within the mold. Following this operation, the object is ejected from the mold.
- Eject the part.
- Repeat with the next part.