Vacuum casting or vacuum duplication uses a master model produced with 3D printing, stereolithography or CNC machining to obtain a silicone mold. This mold makes it possible to obtain a few dozen parts in material close to the final material, making vacuum casting perfect for pre-series.
The principle of vacuum casting or duplication
The procedure of vacuum casting is a type of low-pressure vacuum injection manufacturing or vacuum duplication. It involves injecting material into a pre-prepared silicone mold. This technique makes it possible to obtain multiple parts from a single mold. It, therefore, results in significant economies of scale. However, one mold can be used a limited number of times. This depends on the quality of the mold and the geometry of the parts.
Finally, the use of the vacuum machine makes it possible to remove air from the material and prevent the formation of air bubbles that would make the parts fragile.
The operation of vacuum casting
In the first step, a model master is produced into which the silicone is poured to obtain mold. In the second step, the impression of this silicone mold is filled using polyurethane resins by means of a specific vacuum casting machine to obtain the desired parts.
The major steps in vacuum casting
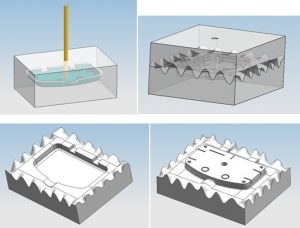
First step: creating the silicone mold
- A master part is made by stereolithography, 3D printing or CNC machining.
- This master part is placed in a chassis in which liquid silicone resin is poured.
- Once the silicone has cured, the silicone is cut along the separation plan, and the master part is removed from the mold.
Second step: production of series parts
- Once the silicone mold is replaced in the machine, the selected material is then injected under a vacuum.
- The resin is then dried. Once cured, the mold is opened to remove the finished part.
Once the parts have been produced, it is possible to add finishes such as overmolding and additions of inserts.