How to draw a plastic part
The importance of 3D design
The phase of defining the design of the part must take account of the specifications of the part’s environment and also the options for industrialization. In fact, the design office must draw a plastic part whose geometry allows an optimal end use while avoiding technical stresses during production as much as possible. The various parameters such as aesthetics, rendering, and physical characteristics depend on the technologies (silicone mold making, 3D plastic machining, etc.) and materials used to produce the 3D prototypes. These production techniques and materials used to manufacture a custom plastic part also determine the renderings and finishes that can be applied.

The creation of the design is the first step in the production of visual and functional prototypes in rapid plastic prototyping.
Geometry
Some rapid prototyping rules for the design of a part:
– Thicknesses: a part that is too thin has a significant risk of breakage and deformation. A thickness of 1.5 mm is thus considered the minimum to prevent the part from breaking. The addition of support structures is also recommended to reinforce a thin part.
– Draft angles: these are used in vacuum casting to facilitate unmoulding. Conversely, undercuts should be avoided for the same reason. In addition, manufacturing a plastic prototype using stereolithography or another additive manufacturing technique will not provide information about manufacturability during industrialization. 3D printing and thermoplastic injection molding are indeed very different production processes.
– Size: parts that are too large must be manufactured by cutting and gluing in plastic machining. If the part requires too many cutting and gluing operations, it may have a major risk of fragility or even be impossible to create. On the other hand, parts that are too small will also be difficult or infeasible to produce (inability to respect visual details).
The manufacturing process
The techniques and materials should be selected carefully. In fact, the possible renderings and finishes will depend on the technology and the material used to design the part. For example, PC and PMMA materials are naturally transparent, and CNC machining materials generally cannot be painted. In addition, the manufacturing technology and plastic materials will offer parts with different physical, chemical and mechanical characteristics. Silicone molding will thus have to be used to produce a flexible part.
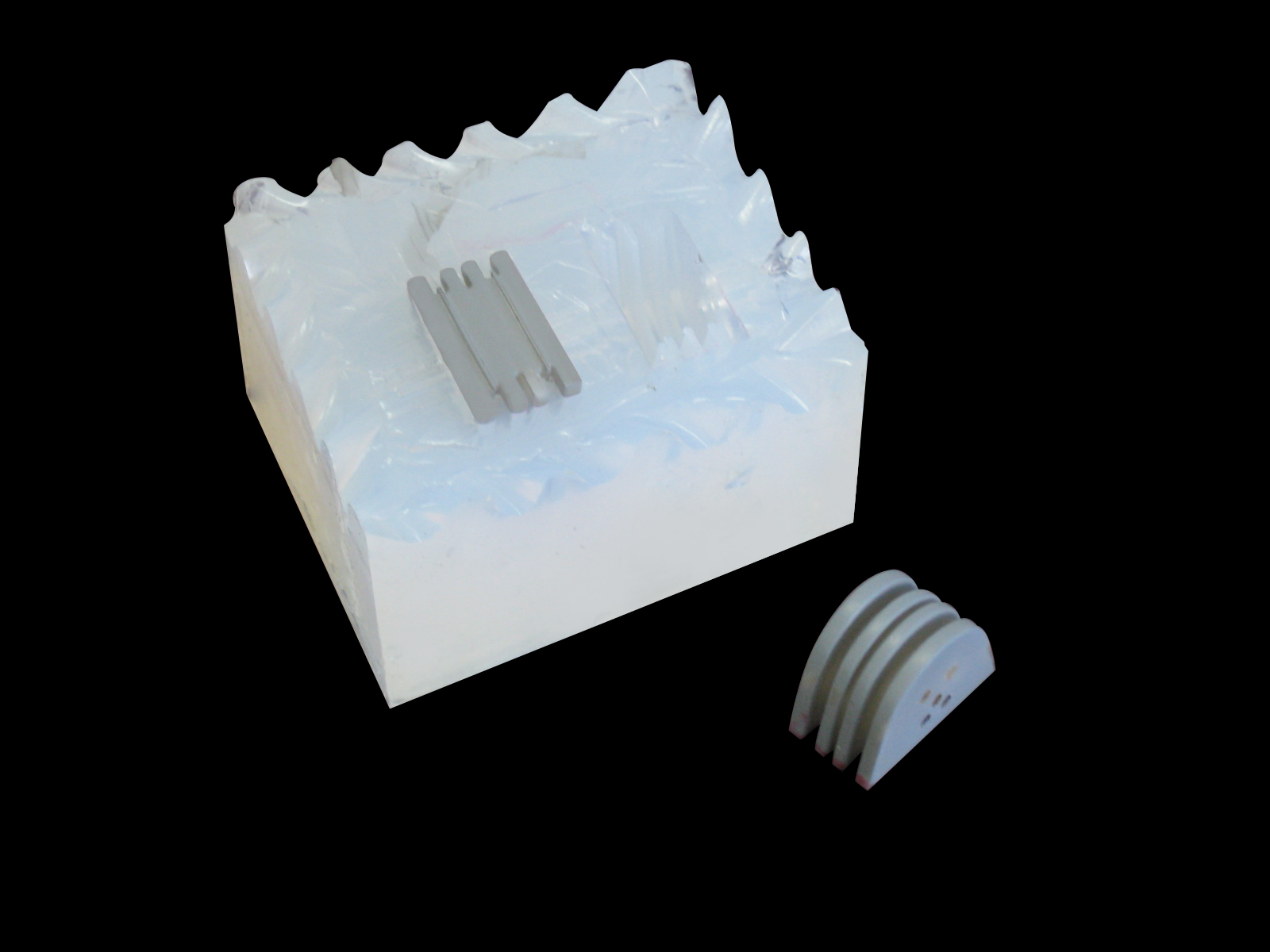 Vacuum casting mold for small series production of technical plastic parts |
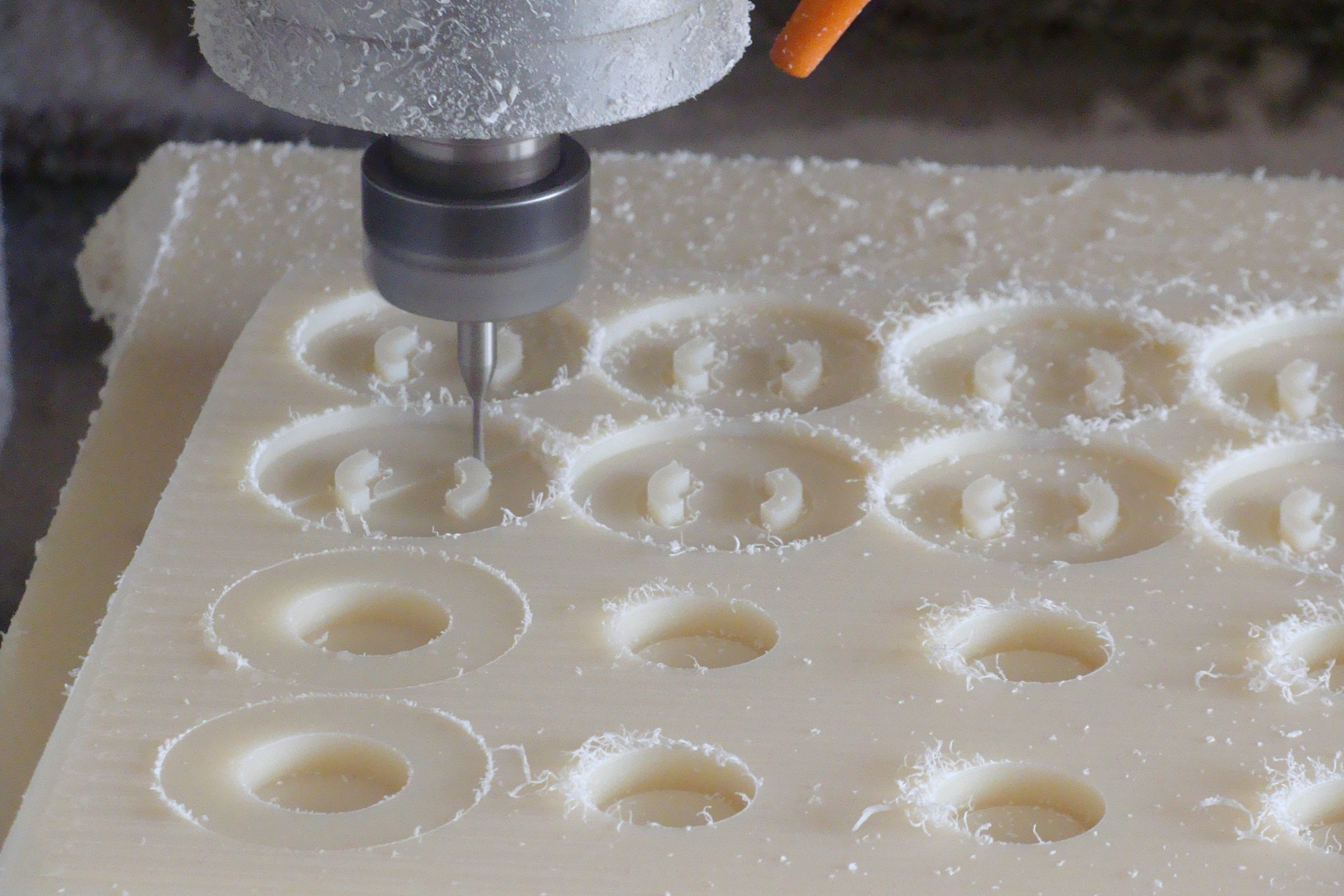 Production of a plastic handle via CNC machining |
Rendering
The color of the parts can be obtained in three ways:
- By applying a paint coat to the surface of the prototype to mimic a RAL or Pantone color.
- By mass dyed color finishing, by adding a dye to the liquid material before injecting it into the silicone mold.
- Without finishing, i.e. with the natural color of the material.
Finishes
The appearance and texture of the parts can have different types:
- Matte by means of more or less strong sandblasting,
- Smooth with a high-polishing finish allowing the removal of rough edges after machining of 3D prototypes,
- Glossy finish with special paint,
- In soft touch to obtain a soft texture, slightly similar to rubber,
- Mirror finishing to produce transparent plastic parts,
- Galvanization for a chrome-plated visual appearance, etc.
In conclusion
Design is one of the first steps of 3D rapid prototyping and one of the most important since it determines the following steps. In fact, the geometry of the part must meet the specifications by limiting the technical stresses during production. In addition, it defines which technologies can be used to manufacture the prototypes and low volume plastic parts. Each plastic prototype manufacturing technology has a certain number of materials available, and therefore renderings and finishes. The visual and mechanical characteristics, therefore, depend on the design of the prototype.
